Routing Information Protocol Version 2
1: Which three fields are new to the RIPv2 message format?
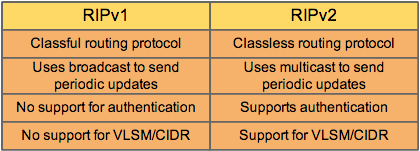
*** The Route Tag field, the Subnet Mask field, and the Next Hop field are RIPv2
extensions that do not exist in RIPv1 messages. The basic format of the RIP
message remains unchanged between the two versions; version 2 merely uses
fields that are unused in version 1.
2: Besides the extensions defined by the three fields of question 1, what
are the other two major changes from RIPv1?
***In addition to the functions that use the new fields, RIPv2 supports
authentication and multicast updates.
3: What is the multicast address used by RIPv2? What is the advantage of
multicasting messages over broadcasting them?
***RIPv2 uses the multicast address 224.0.0.9. Multicasting of routing messages
is better than broadcasting because hosts and non-RIPv2 routers will ignore the
multicast messages .
4: What is the purpose of the Route Tag field in the RIPv2 message?
*** When another routing protocol uses the RIPv2 domain as a transit domain,
the protocol external to RIPv2 can use the Route Tag field to communicate
information to its peers on the other side of the RIPv2 domain.
5: What is the purpose of the Next Hop field?
*** The Next Hop field is used to inform other routers of a next-hop address on
the same multiaccess network that is metrically closer to the destination than the
originating router.
6: What is the UDP port number used by RIPv2?
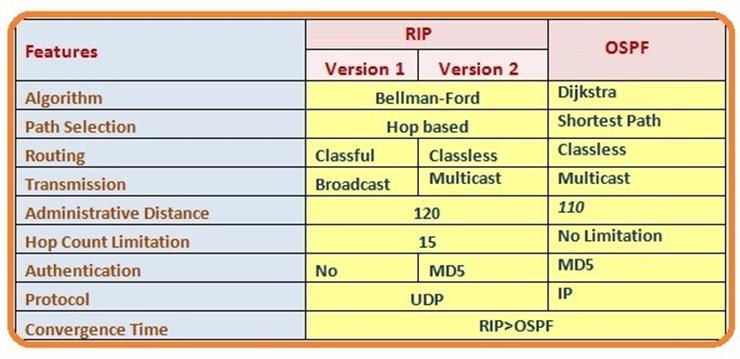
***RIPv2 uses the same UDP port number as RIPv1, port number 520.
7: Which one feature must a routing protocol have to be a classless routing
protocol?
***A classless routing protocol does not consider the major network address in its
route lookups, but just looks for the longest match.
8: Which one feature must a routing protocol have to use VLSM?
*** To support VLSM, a routing protocol must be able to include the subnet mask
of each destination address in its updates.
9: Which two types of authentication are available with Cisco’s RIPv2? Are
they both defined in RFC 1723?
*** Cisco’s implementation of RIPv2 supports clear-text authentication and MD5
authentication. Only clear-text authentication is defined in RFC 1723.