OSPF Interview Questions
1: What is an OSPF neighbor?
*** From the perspective of an OSPF router, a neighbor is another OSPF router
that is attached to one of the first router’s directly connected links.
2: What is an OSPF adjacency?
***An OSPF adjacency is a conceptual link to a neighbor over which LSAs can
be sent.
3: What is an LSA? How does an LSA differ from an OSPF Update packet?
***A router originates a link state advertisement to describe one or more
destinations. An OSPF Update packet transports LSAs from one neighbor to
another. Although LSAs are flooded throughout an area or OSPF domain,
Update packets never leave a data link.
4: What is a link state database? What is link state database
synchronization?
***The link state database is where a router stores all the OSPF LSAs it knows
of, including its own. Database synchronization is the process of ensuring that all
routers within an area have identical link state databases.
5: What is the default HelloInterval?
***The default OSPF HelloInterval is 10 seconds.
6: What is the default RouterDeadInterval?
***The default RouterDeadInterval is four times the HelloInterval.
7: What is a Router ID? How is a Router ID determined?
***A Router ID is an address by which an OSPF router identifies itself. It is either
the numerically highest IP address of all the router’s loopback interfaces, or if no
loopback interfaces are configured, it is the numerically highest IP address of all
the router’s LAN interfaces.
8: What is an area?
***An area is an OSPF sub-domain, within which all routers have an identical link
state database.
9: What is the significance of area 0?
***Area 0 is the backbone area. All other areas must send their inter-area traffic
through the backbone.
10: What is MaxAge?
***MaxAge, 1 hour, is the age at which an LSA is considered to be obsolete.
11: What are the five OSPF packet types? What is the purpose of each type?
*** The five OSPF packet types, and their purposes, are:
Hellos, which are used to discover neighbors, and to establish and maintain
adjacencies
Updates, which are used to send LSAs between neighbors
Database Description packets, which a router uses to describe its link state
database to a neighbor during database synchronization
Link State Requests, which a router uses to request one or more LSAs from a
neighbor’s link state database
Link State Acknowledgments, used to ensure reliable delivery of LSAs
12:What are LSA types 1 to 5 and LSA type 7? What is the purpose of each
type?
*** The most common LSA types and their purposes are:
Type 1 (Router LSAs) are originated by every router and describe the originating
router, the router’s directly connected links and their states, and the router\xd5 s
neighbors.
Type 2 (Network LSAs) are originated by Designated Routers on multiaccess
links and describe the link and all attached neighbors.
Type 3 (Network Summary LSAs) are originated by Area Border Routers and
describe inter-area destinations.
Type 4 LSAs (ASBR Summary LSAs) are originated by Area Border Routers to
describe Autonomous System Boundary Routers outside the area.
Type 5 (AS External LSAs) are originated by Autonomous System Boundary
Routers to describe destinations external to the OSPF domain.
Type 7 (NSSA External LSAs) are originated by Autonomous System Boundary
Routers within not-so-stubby areas.
13: What are the four OSPF router types?
***The four OSPF router types are:
# Internal Routers, whose OSPF interfaces all belong to the same area
# Backbone Routers, which are Internal Routers in Area 0
# Area Border Routers, which have OSPF interfaces in more than one area
# Autonomous System Boundary Routers, which advertise external routes into
the OSPF domain
14: What are the four OSPF path types?
***The four OSPF path types are:
Intra-area paths
Inter-area paths
Type 1 external paths
Type 2 external paths
15: What are the five OSPF network types?
*** The five OSPF network types are:
i)Point-to-point networks
ii) Broadcast networks
iii) Non-broadcast multi-access (NBMA) networks
iv) Point-to-multipoint networks
v) Virtual links
16: What is a Designated Router?
***A Designated Router is a router that represents a multiaccess network, and
the routers connected to the network, to the rest of the OSFP domain.
17: How does a Cisco router calculate the outgoing cost of an interface?
***Cisco IOS calculates the outgoing cost of an interface as 108/BW, where BW
is the configured bandwidth of the interface.
18: What is a partitioned area?
***An area is partitioned if one or more of its routers cannot send a packet to the
area’s other routers without sending the packet out of the area.
19: What is a virtual link?
*** A virtual link is a tunnel that extends an OSPF backbone connection through
a non-backbone area.
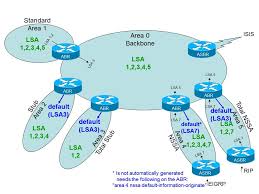
20: What is the difference between a stub area, a totally stubby area, and a
not-so-stubby area?
***A stub area is an area into which no type 5 LSAs are flooded. A totally stubby
area is an area into which no type 3, 4, or 5 LSAs are flooded, with the exception
of type 3 LSAs to advertise a default route. Not-so-stubby areas are areas
through which external destinations are advertised into the OSPF domain, but
into which no type 5 LSAs are sent by the ABR.
21: What is the difference between OSPF network entries and OSPF router
entries?
*** OSPF network entries are entries in the route table, describing IP
destinations. OSPF router entries are entries in a separate route table that record
only routes to ABRs and ASBRs.
22: Why is type 2 authentication preferable over type 1 authentication?
***Type 2 authentication uses MD5 encryption, whereas type 1 authentication
uses clear-text passwords.
23: Which three fields in the LSA header distinguish different LSAs? Which
three fields in the LSA header distinguish different instances of the same
LSA?
***The three fields in the LSA header that distinguish different LSAs are the
Type, Advertising Router, and the Link State ID fields. The three fields in the LSA
header that distinguish different instances of the same LSA are the Sequence
Number, Age, and Checksum fields

hi all, how i can see he entire toics bcoz it shows incomplete.....kindly help in this regard