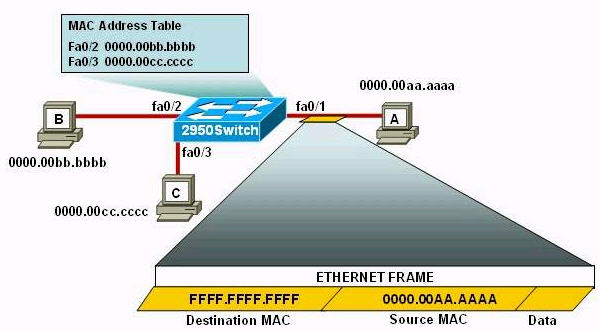
Question 9
A network administrator needs to configure port security on a switch. Which two statements are true? (Choose two)
A. The network administrator can apply port security to dynamic access ports
B. The network administrator can configure static secure or sticky secure mac addresses in the voice vlan.
C. The sticky learning feature allows the addition of dynamically learned addresses to the running configuration.
D. The network administrator can apply port security to EtherChannels.
E. When dynamic mac address learning is enabled on an interface, the switch can learn new addresses up to the maximum defined.
Answer: C E
Question 10
Refer to the exhibit. Which statement is true?
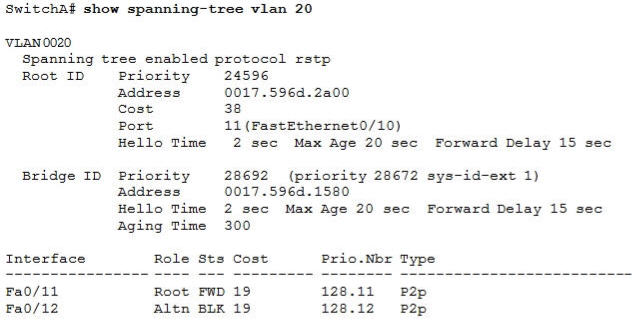
A. The Fa0/11 role confirms that SwitchA is the root bridge for VLAN 20.
B. VLAN 20 is running the Per VLAN Spanning Tree Protocol.
C. The MAC address of the root bridge is 0017.596d.1580.
D. SwitchA is not the root bridge, because not all of the interface roles are designated.
Answer: D
Explanation
Only non-root bridge can have root port. Fa0/11 is the root port so we can confirm this switch is not the root bridge -> A is not correct.
From the output we learn this switch is running Rapid STP, not PVST -> B is not correct.
0017.596d.1580 is the MAC address of this switch, not of the root bridge. The MAC address of the root bridge is 0017.596d.2a00 -> C is not correct.
All of the interface roles of the root bridge are designated. SwitchA has one Root port and 1 Alternative port so it is not the root bridge -> D is correct.
Question 12
A network administrator wants to ensure that only the server can connect to port Fa0/1 on a Catalyst switch. The server is plugged into the switch Fa0/1 port and the network administrator is about to bring the server online. What can the administrator do to ensure that only the MAC address of the server is allowed by switch port Fa0/1? (Choose two)
A. Configure port Fa0/1 to accept connections only from the static IP address of the server.
B. Employ a proprietary connector type on Fa0/1 that is incompatible with other host connectors.
C. Configure the MAC address of the server as a static entry associated with port Fa0/1.
D. Bind the IP address of the sewer to its MAC address on the switch to prevent other hosts from spoofing the server IP address.
E. Configure port security on Fa0/1 to reject traffic with a source MAC address other than that of the server.
F. Configure an access list on the switch to deny server traffic from entering any port other than Fa0/1.
Answer: C E
Explanation
We can”configure the MAC address of the server as a static entry associated with port Fa0/1″ with this command:
Switch(config-if)#switchport port-security mac-address sticky 0000.00AA.AAAA.AAAA
and “configure port security on Fa0/1 to reject traffic with a source MAC address other than that of the server” with these commands:
Switch(config-if)#switchport port-security maximum 1 (only allow 1 MAC address and that is the static MAC address)
Also we often define what will the switch do if the security is violated:
Switch(config-if)#switchport port-security violation shutdown
Question 13
The network security policy requires that only one host be permitted to attach dynamically to each switch interface. If that policy is violated, the interface should shut down. Which two commands must the network administrator configure on the 2950 Catalyst switch to meet this policy? (Choose two)
A. Switch1(config-if)#switchport port-security maximum 1
B. Switch1(config)#mac-address-table secure
C. Switch1(config)#access-list 10 permit ip host
D. Switch1(config-if)#switchport port-security violation shutdown
E. Switch1(config-if)#ip access-group 10
Answer: A D
Question 1
In which circumstance are multiple copies of the same unicast frame likely to be transmitted in a switched LAN?
A. after broken links are re-established
B. in an improperly implemented redundant topology
C. when upper-layer protocols require high reliability
D. during high traffic periods
E. when a dual ring topology is in use
Answer: B
Explanation
If we connect two switches via 2 or more links and do not enable STP on these switches then a loop (which creates multiple copies of the same unicast frame) will occur. It is an example of an improperly implemented redundant topology.
Question 2
An administrator would like to configure a switch over a virtual terminal connection from locations outside of the local LAN. Which of the following are required in order for the switch to be configured from a remote location? (Choose two)
A. The switch must be configured with an IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway.
B. The switch must be connected to a router over a VLAN trunk.
C. The switch must be reachable through a port connected to its management VLAN.
D. The switch console port must be connected to the Ethernet LAN.
E. The switch management VLAN must be created and have a membership of at least one switch port.
F. The switch must be fully configured as an SNMP agent.
Answer: A C
Explanation
In order to remote access to a switch from outside of the local LAN (in a different subnet) we have to:
+ Configure an IP address on a VLAN on that switch, this VLAN is known as the management VLAN (it is usually VLAN 1)
+ Specify the default gateway for that switch so that it can send traffic to this gateway
Below shows an example of configuring remote access for a switch (suppose the management VLAN on the switch is 192.168.1.10/24 and the default-gateway IP address is 192.168.1.254)
Switch(config)#ip default-gateway 192.168.1.254
Switch(config)#interface vlan 1
Switch(config)#ip address 192.168.1.10 255.255.255.0
Switch(config)#no shutdown
Question 3
Refer to the exhibit. A junior network administrator was given the task of configuring port security on SwitchA to allow only PC_A to access the switched network through port fa0/1. If any other device is detected, the port is to drop frames from this device. The administrator configured the interface and tested it with successful pings from PC_A to RouterA, and then observes the output from these two show commands.
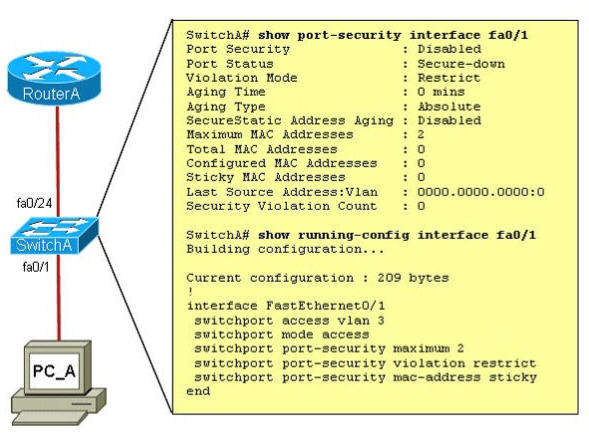
Which two of these changes are necessary for SwitchA to meet the requirements? (Choose two)
A. Port security needs to be globally enabled.
B. Port security needs to be enabled on the interface.
C. Port security needs to be configured to shut down the interface in the event of a violation.
D. Port security needs to be configured to allow only one learned MAC address.
E. Port security interface counters need to be cleared before using the show command.
F. The port security configuration needs to be saved to NVRAM before it can become active.
Answer: B D
Explanation
As we see in the output, the “Port Security” is in “Disabled” state (line 2 in the output). To enable Port security feature, we must enable it on that interface first with the command:
SwitchA(config-if)#switchport port-security
-> B is correct.
Also from the output, we learn that the switch is allowing 2 devices to connect to it (switchport port-security maximum 2) but the question requires allowing only PC_A to access the network so we need to reduce the maximum number to 1 -> D is correct.
Question 4
A company implements video conferencing over IP on their Ethernet LAN. The users notice that the network slows down, and the video either stutters or foils completely. What is the most likely reason for this?
A. minimum cell rate (MCR)
B. quality of service (QoS)
C. modulation
D. packet switching exchange (PSE)
E. reliable transport protocol (RTP)
Answer: B
Explanation
If the QoS is not configured correctly on the network (for example configure your network’s bandwidth below the bandwidth assigned by your ISP) can slow down all your traffic.
Question 8
Refer to the exhibit. Some 2950 series switches are connected to the conference area of the corporate headquarters network. The switches provide two to three jacks per conference room to host laptop connections for employees who visit the headquarters office. When large groups of employees come from other locations, the network administrator often finds that hubs have been connected to wall jacks in the conference area although the ports on the access layer switches were not intended to support multiple workstations.
What action could the network administrator take to prevent access by multiple laptops through a single switch port and still leave the switch functional for its intended use?
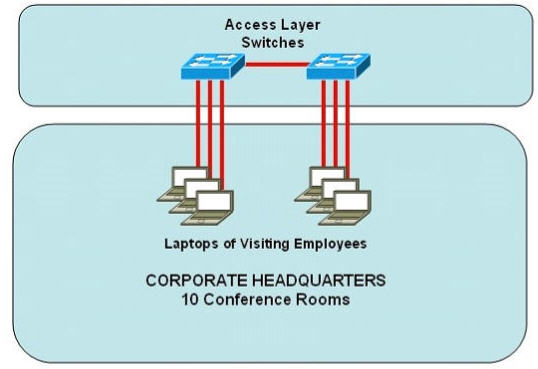
A. Configure static entries in the switch MAC address table to include the range of addresses used by visiting employees.
B. Configure an ACL to allow only a single MAC address to connect to the switch at one time.
C. Use the mac-address-table 1 global configuration command to limit each port to one source MAC address.
D. Implement Port Security on all interfaces and use the port-security maximum 1 command to limit port access to a single MAC address
E. Implement Port Security on all interfaces and use the port-security mac-address sticky command to limit access to a single MAC address
F. Implement Port Security at global configuration mode and use the port-security maximum 1 command to allow each switch only one attached hub
Answer: D
Explanation
The Port Security filters frames based on its MAC so it can effectively prevent people connecting to the switch via hubs.
Question 9
Which of the following statements are true regarding bridges and switches? (Choose 3)
A. Switches are primarily software based while bridges are hardware based.
B. Both bridges and switches forward Layer 2 broadcasts.
C. Bridges are frequently faster than switches.
D. Switches have a higher number of ports than most bridges.
E. Bridges define broadcast domains while switches define collision domains.
F. Both bridges and switches make forwarding decisions based on Layer 2 addresses.
Answer: B D F
Question 10
A network administrator must configure 200 switch ports to accept traffic from only the currently attached host devices. What would be the most efficient way to configure MAC-level security on all these ports?
A. Visually verify the MAC addresses and then telnet to the switches to enter the switchport-port security mac-address command.
B. Have end users e-mail their MAC addresses. Telnet to the switch to enter the switchport-port security mac-address command.
C. Use the switchport port-security MAC address sticky command on all the switch ports that have end devices connected to them.
D. Use show mac-address-table to determine the addresses that are associated with each port and then enter the commands on each switch for MAC address port-security.
Answer: C
Explanation
We can use the “interface range” command (for example “interface range FastEthernet 0/1 – 48″) to configure many ports as the same time and use the “port-security MAC address sticky” command (without a specific MAC address) to dynamically learn the attached MAC Address and place it into the switch’s running-configuration -> C is correct.
Which two of these changes are necessary for SwitchA to meet the requirements? (Choose two)
A. Port security needs to be globally enabled.
B. Port security needs to be enabled on the interface.
C. Port security needs to be configured to shut down the interface in the event of a violation.
D. Port security needs to be configured to allow only one learned MAC address.
E. Port security interface counters need to be cleared before using the show command.
F. The port security configuration needs to be saved to NVRAM before it can become active.
Answer: B D
Explanation
As we see in the output, the “Port Security” is in “Disabled” state (line 2 in the output). To enable Port security feature, we must enable it on that interface first with the command:
SwitchA(config-if)#switchport port-security
-> B is correct.
Also from the output, we learn that the switch is allowing 2 devices to connect to it (switchport port-security maximum 2) but the question requires allowing only PC_A to access the network so we need to reduce the maximum number to 1 -> D is correct.
Question 4
A company implements video conferencing over IP on their Ethernet LAN. The users notice that the network slows down, and the video either stutters or foils completely. What is the most likely reason for this?
A. minimum cell rate (MCR)
B. quality of service (QoS)
C. modulation
D. packet switching exchange (PSE)
E. reliable transport protocol (RTP)
Answer: B
Explanation
If the QoS is not configured correctly on the network (for example configure your network’s bandwidth below the bandwidth assigned by your ISP) can slow down all your traffic.